Entwurf des Merger-Integration-Projekts
Sachziele und Formalziele der Aufgabe
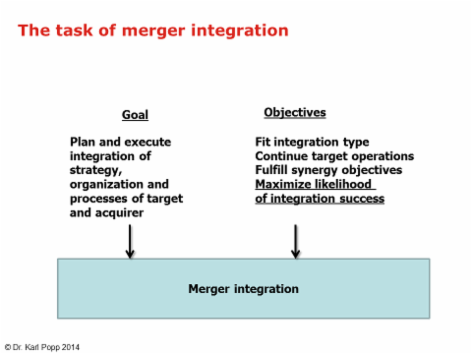
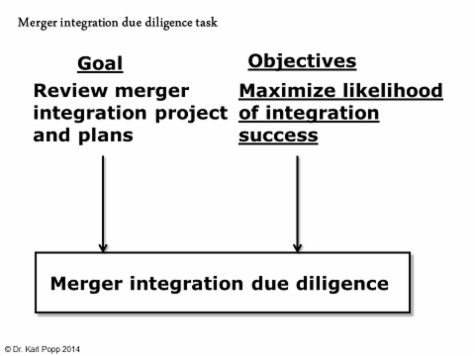
Die Aufgabe hat das/die folgende(n) Sachziel(e):
Entwurf eines Integrationsprojektplans: vorbereitet
Die Aufgabe hat folgende Formalziele
Integrationserfolg: maximiert
Synergie: maximiert
Risiko: minimiert
Automatisierbarkeit
Diese Aufgabe ist teilweise automatisierbar. Projektplanungsanwendungen stehen für die Aktionen "Projekt planen und simulieren" und "Kritischen Pfad berechnen" zur Verfügung.
Beschreibung der Aufgabe
Es ist wichtig, sich daran zu erinnern, dass der Begriff "Projekt" impliziert, dass wir ein professionelles Management der Integration durch professionelle Projektmanager haben, die Erfahrung mit komplexen Projekten haben und mit den Fähigkeiten eines zertifizierten Projektmanagers ausgestattet sind. Der Begriff "Projekt" impliziert auch, dass wir einen Projektstrukturplan mit den im Projekt zu erfüllenden Aufgaben haben. Kaufende Unternehmen, die häufig Übernahmen tätigen, verfügen über eine Vorlage für einen Projektstrukturplan, die sie an jedes der neuen Integrationsprojekte anpassen. Dadurch wird die Vollständigkeit in Bezug auf die Abdeckung aller Integrationsthemen gewährleistet und wir können auch beurteilen, ob wir über ausreichende Ressourcen verfügen und ob die Ressourcen wissen, was bei der Integration zu tun ist. Bei dieser Aufgabe wird die Abfolge der Integrationsaktivitäten im Integrationsprojektplan festgehalten. Er bestimmt, wann die einzelnen Integrationsschritte durchgeführt werden können und ob zu diesem Zeitpunkt genügend Ressourcen zur Verfügung stehen, um sie durchzuführen. Dabei werden die Abhängigkeiten zwischen den einzelnen Integrationsaktivitäten und der Ressourcensituation berücksichtigt. Kritische Pfade werden analysiert. Dabei spielen IT-Integrationsaktivitäten eine besondere Rolle, von denen viele andere Aktivitäten abhängen. Mögliche Risiken werden im Integrationsplan Risiken aufgelistet, Abschwächungen werden geplant und die Risiken werden im folgenden Integrationsprojekt verfolgt.
Die Aufgabe arbeitet u.a. auf folgenden Datenobjekttypen:
Integrationsprojekt, Integrationsprojektplan, Integrationsplanrisiko, Integrationsbudget, Entwurf des Integrationsprojektplans, Integrationsprojektressourcen, Organisationsplan des Ziels, Einkäuferorganisation, Entwurf des finanziellen Integrationsplans, Aufgabe des Entwurfs des Integrationsplans für Kultur, Entwurf des strategischen Integrationsplans, Entwurf des Produktionsintegrationsplans, Entwurf des Plans für zukünftige Personalkosten, Mapping der Zielstellen auf die Stellenbeschreibungen der NewCo, Entwurf des HR-Kommunikationsplans, Entwurf des HR-Onboarding-Plans, Entwurf des HR-Schulungsplans, Entwurf des Kulturintegrationsplans, Entwurf des steuerlichen Integrationsplans, Entwurf des Geschäftsmodellintegrationsplans, Entwurf des Operationsintegrationsplans, Entwurf des technischen Integrationsplans, Entwurf des GTM-Integrationsplans, Entwurf des IP-Integrationsplans, Entwurf des HR-Integrationsplans, Entwurf des rechtlichen Integrationsplans, Entwurf des Integrationsplans für Partnerschaften, Entwurf des IT-Integrationsplans, Entwurf des Integrationsplans.
Die Aufgabe wird u.a. mit den folgenden Fragen durchgeführt:
Decken die Teilprojekte des Integrationsprojekts alle Aspekte des Integrationsplans ab?
Welche zeitlichen Abhängigkeiten bestehen zwischen den Teilintegrationsplänen?
Welche sequenzbasierten Abhängigkeiten bestehen zwischen den Teilintegrationsplänen?
Ist die zeitliche Abfolge der Integrationsaktivitäten sinnvoll?
Sind alle Stakeholder des Integrationsprojekts und ihre Beteiligung definiert?
Wie motivieren wir die Stakeholder des Integrationsprojekts?
Wie motivieren wir die Schlüsselakteure des Integrationsprojekts?
Wie zeichnen wir die Akteure und Schlüsselakteure des Integrationsprojekts aus?
Planen wir, Meilensteine und Erfolge des Integrationsprojekts zu feiern, und wann?
Sind alle erforderlichen Ressourcen zum geeigneten Zeitpunkt verfügbar?
Beeinträchtigt die Belastung durch die Integrationsaktivitäten zu irgendeinem Zeitpunkt die Operationen und Ergebnisse der NewCo?
Wie vermeiden wir eine Arbeitsüberlastung der Hauptakteure im Integrationsprojekt?
Welche zeitlichen Verzögerungen erwarten wir bei dem Projekt?
Wie wirkt sich die Mitbestimmung auf den Projektfortschritt aus?
Wurden verschiedene Szenarien von Zeitverschiebungen in einzelnen Teilprojekten, insbesondere bei der IT-Integration, simuliert?
Wie reagieren wir auf ungeplante Veränderungen während des Projekts, wie z.B. massive Preissenkungen auf den Absatzmärkten, eine Pandemie oder einen wirtschaftlichen Abschwung?
Welche Integrationsaktivitäten sollten vor dem ersten Tag beginnen und wie und von wem werden sie durchgeführt?
Welches sind die Voraussetzungen, um den Abschluss der Integration zu erklären?
Das alles und mehr in meinem neuen Buch: